Assessment of the Functional State of the Cardiovascular System in Patients with Diabetes and Hypertension Who Have Recovered from COVID-19
Keywords:
Cardiovascular function, diabetes, hypertension, COVID-19 recovery, myocardial injury, endothelial dysfunction, arrhythmias, post-COVID syndromeAbstract
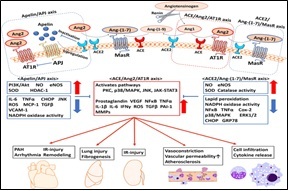
Patients with diabetes and hypertension who recover from COVID-19 face elevated cardiovascular risks, necessitating a comprehensive evaluation of their cardiovascular functional state. This review synthesizes current evidence on the functional changes in the cardiovascular system post-SARS-CoV-2 infection among this high-risk group, focusing on myocardial injury, endothelial dysfunction, and persistent symptoms. SARS-CoV-2 exacerbates pre-existing vulnerabilities through direct viral invasion, systemic inflammation, and hypercoagulability, leading to increased incidences of myocardial fibrosis, left ventricular dysfunction, and arrhythmias. Diagnostic tools such as echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and biomarkers like troponin and NT-proBNP reveal these alterations, with global data indicating a significant public health challenge—over 422 million people with diabetes and 1.28 billion with hypertension are affected. This study examines pathophysiological mechanisms, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, and long-term outcomes, highlighting the need for tailored management strategies. While evidence underscores heightened morbidity, gaps persist in individualized treatment and long-term follow-up protocols. These findings aim to inform clinicians in optimizing care, reducing complications, and improving prognosis for this vulnerable population, with implications for global health systems addressing post-COVID sequelae.
References
World Health Organization, "Diabetes fact sheet," 2022.
World Health Organization, "Hypertension fact sheet," 2021.
S. Kumar and P. Singh, "Post-COVID cardiac complications: An overview," Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Eng., Vol.9, pp.45-52, 2022.
M. Nishiga et al., "COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: From basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives," Nat. Rev. Cardiol., Vol.17, pp.543-558, 2020.
S. K. Sharma and R. Gupta, "Impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular health: A review," Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Trends, Vol.7, pp.123-130, 2021.
P. Libby and T. Luscher, "COVID-19 is, in the end, an endothelial disease," Eur. Heart J., Vol.41, pp.3038-3044, 2020.
Y. Xie et al., "Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19," Nat. Med., Vol.28, pp.583-590, 2022.
S. Bangalore et al., "COVID-19-associated cardiovascular complications," N. Engl. J. Med., Vol.382, pp.1709-1721, 2020.
T. Guo et al., "Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with COVID-19," JAMA Cardiol., Vol.5, pp.811-818, 2020.
N. Tang et al., "Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients," J. Thromb. Haemost., Vol.18, pp.844-847, 2020.
V. O. Puntmann et al., "Outcomes of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients recently recovered from COVID-19," JAMA Cardiol., Vol.5, pp.1265-1273, 2020.
D. Lakkireddy et al., "Arrhythmias in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review," Am. J. Cardiol., vol. 135, pp. 150-159, 2020.
T. Guo et al., "Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with COVID-19," JAMA Cardiol., Vol.5, pp.811-818, 2020.
N. Tang et al., "Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients," J. Thromb. Haemost., Vol.18, pp.844-847, 2020.
S. K. Sharma and R. Gupta, "Impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular health: A review," Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Trends, Vol.7, pp.123-130, 2021.
S. Kumar and P. Singh, "Post-COVID cardiac complications: An overview," Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Eng., Vol.9, pp.45-52, 2022.
M. Iwasaki et al. “Inflammation Triggered by SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 Augment Drives Multiple Organ Failure of Severe COVID-19: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications,” Inflammation, Vol.44, pp.13–34, 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





